Blockchain Technology and Penetration Testing
Sukesh Goud
Dec 4, 2023
•
5 Min
Sukesh Goud
Dec 4, 2023
•
5 Min
Blockchain technology is an advanced database mechanism that allows transparent information sharing within a business network. A blockchain database stores data in blocks that are linked together in a chain,
Blockchain operates on a decentralized and distributed ledger system, utilizing a combination of cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms.
The data is chronologically consistent because you cannot delete or modify the chain without consensus from the network. As a result, you can use blockchain technology to create an unalterable or immutable ledger for tracking orders, payments, accounts, and other transactions.
How to work ,
On its most basic level, blockchain technology is a transaction ledger on a massive scale.
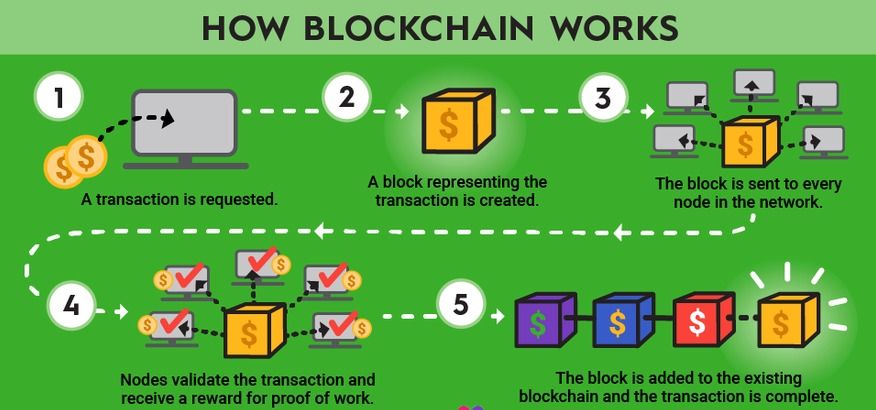 https://www.fool.com/terms/b/blockchain/
https://www.fool.com/terms/b/blockchain/
Here are key components and concepts associated with blockchain:
Blockchains can manage any system that involves digital data points and/or transactions.

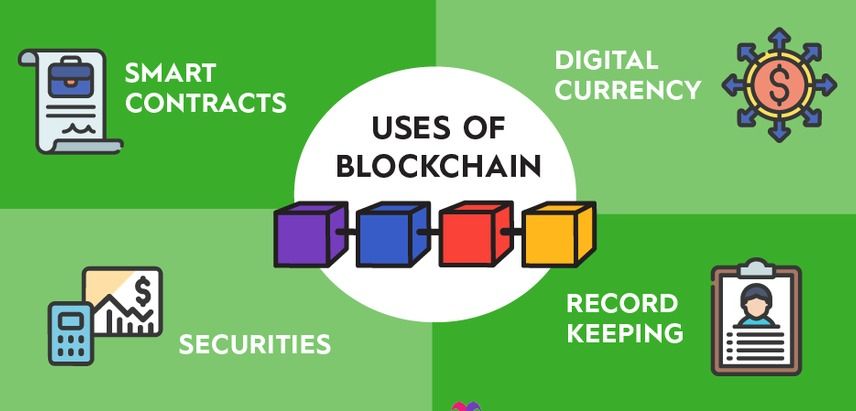 https://www.fool.com/terms/b/blockchain/
https://www.fool.com/terms/b/blockchain/
Which industries use blockchain?
Blockchain security refers to the measures and practices implemented to protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of blockchain systems and their associated data. Given that blockchain operates on a decentralized and transparent network, security is crucial to prevent unauthorized access, manipulation, and other potential threats. Here are key aspects of blockchain security
Blockchain is an immutable ledger with no involvement of a third-party organization. It also uses cryptography to hide some details. So hackers find it almost impossible to tamper with the blocks. But there are some loopholes that allow the malicious users to perform malicious activities as blockchain networks are not immune to cyberattacks and fraud.
Blockchain penetration testing involves systematically assessing the security of a blockchain system to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that could be exploited by malicious actors. Here’s a detailed process for conducting blockchain penetration testing:
Consensus Mechanism Evaluation: Assess the resilience of the consensus mechanism against potential attacks, such as 51% attacks or network partitioning.
Share